Inception Net
Paper_Review_InceptionNet=GoogLeNet
Going Deeper with Convolutions AKA Inception by Szegedy et al.
https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Szegedy_Going_Deeper_With_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf
논문의 중요 내용을 잘라서 붙이고 + 개인적으로 이해한 내용을 정리했음.
요약: Inception Architecture라고도 불림. 2014년에 나온 CNN기반의 image classification and object detection 아키텍처. 파라미터 수를 크게 줄이면서 동시에 NN의 depth와 widtd을 아주 깊고 넓게 구성하면서 성능의 발전까지 이끌어 냄. 생물학에서 correlation을 가진 정보들을 가진 뉴런들끼리 밀집한다는 이론에서 아이디어를 얻었음. 비슷한 정보를 가진 파라미터들을 weghted sum으로 합쳐서 파라미터의 수를 줄이는 방법으로 구현해서 파라미터의 수를 줄임. convolution이 이전 layer의 파라미터를 다음 레이어로 차원을 줄이면서 weight sum으로 표현되는 것을 이용. layer에서 다음 layer으로 넘어갈 때 (1 x 1), (3 x 3), (5 x 5) 필터를 각각 적용한 결과를 concatinate 함. 각 필터의 결과는 inception module이라고 불림. 이전 레이어의 정보들을 다양한 정보 밀집도를 사용해서 가공한 정보를 종합적으로 판단한다고 해석할 수 있을 것 같음. 이 방법으로 파라미터를 적게 유지하면서 깊고 넓게 들어가면서 모델을 학습 시킴. 모델의 코드네임에 inception이 들어간 것은 영화 inceptio의 대사 “We go deeper”에서 따왔다고 함(…).
Iteration 1
Title
Going Deeper with Convolutions
abstract
- use for classification and detection
- improved utilization of the computing resources inside the network
- increased the depth and width of the network while keeping the compu tational budget constant.
- Optimization detail: based on the Hebbian principle and the intuition of multiscale processing
- One particular incarnation: GoogLeNet, a 22 layers deep network. shown great performance increment
figures
- ILSVRC 2014 classification challenge.
- naive version and dimensionality reduction version
- GoogLeNet
- performance: error 6% classification. no exteranl dataset.
Iteration2
introduction
- trained with same data with previous years, but significantly higher performance.
- This acheivements come from the sake of the new ideas!
- even smaller number of parameters.
- object detection: not just naive bigger and deeper network. But with synergy of deep architecture(DNN) and the CNN(computer vision).
- ongoing traction of mobile and embedded computing, the efficiency of our algorithms – especially their power and memory use – gains importance.
- limited memory and power! important these days!
- For most of the experiments, the models were designed to keep a computational budget of 1.5 billion multiply-adds at inference time,…, could be put to real world use, even on large datasets, at a reasonable cost.
- focus on an efficient deep neural network architecture for computer vision
- we introduce a new level of organization in the form of the “Inception module”
- also in the more direct sense of increased network depth.
conclusion
- Our results yield a solid evidence that approximating the expected optimal sparse structure by readily available dense building blocks is a viable method for improving neural networks for computer vision.
- The main advantage of this method is a significant quality gain at a modest increase of computational requirements
- it is expected that similar quality of result can be achieved by much more ex- pensive non-Inception-type networks of similar depth and width. Still, our approach yields solid evidence that mov- ing to sparser architectures is feasible and useful idea in general. inception을 쓰지 않고도, 비슷한 깊이와 너비의 NN도 비슷한 성능을 낼 수는 있겠지만. inception을 쓰면 sparse network들을 사용해서 computation 비용이 많이 감소한다.
더 얻어야 할 정보: approximating the expected optimal sparse structure by readily available dense building blocks
figues
- figure2: naive version and dimension reduction version: performance difference? The idea and approximation to sparse network?
Iteration 3
- read wide and fast
Related work
- Network-in-Network is an approach proposed by Lin et al. [12] 1 by 1 conv
- improve: This allows for not just increasing the depth, but also the width of our networks without a significant performance penalty.
- Lin et al이 1 by 1 convlution을 발표 함. parameter을 줄이고 정보를 압축함. 이게 파라미터를 줄이는 핵심 역할을 함.
- use R-CNN.
- improve: We adopted a similar pipeline in our detec- tion submissions, but have explored enhancements in both stages, such as multi-box [5] prediction for higher object bounding box recall, and ensemble approaches for better categorization of bounding box proposals.
Motivation and High Level Considerations
- 문제 제기
- 성능을 높이는 가장 일반적인 방법: depth와 width을 늘린다.
- 두가지 문제가 발생. 1. performance issue, 2.computation budget issue
- Bigger size typically means a larger number of parame- ters, which makes the enlarged network more prone to over- fitting, especially if the number of labeled examples in the training set is limited. 파라미터가 많아지고 overfitting할 가능성이 커진다.
- The other drawback of uniformly increased network size is the dramatically increased use of computational re- sources. 파라미터가 커지니까 학습할 계산이 많아짐.
- solution
- A fundamental way of solving both of these issues would be to introduce sparsity and replace the fully connected lay- ers by the sparse ones, even inside the convolutions.
- 근본적인 해결책: fully connected layer가 아니라 spare connected layer을 사용해서 overfitting을 막고 파라미터 수를 줄이자.
- 이론
- (theory)Arora et al. [2] Their main re- sult states that if the probability distribution of the dataset is representable by a large, very sparse deep neural network, then the optimal network topology can be constructed layer after layer by analyzing the correlation statistics of the pre- ceding layer activations and clustering neurons with highly correlated outputs.
- Arora et al.에 따르면… 수학적으로… optimal sparese network가 존재한다면(데이터의 분포를 NN으로 표현할 수 있다면), 이전 layer의 output은 다음 layer에 correlat할 것이다.
- 이론을 적용
- Although the strict mathematical proof requires very strong conditions, the fact that this statement resonates with the well known Hebbian principle – neurons that fire together, wire together – suggests that the under- lying idea is applicable even under less strict conditions, in practice.
- Arora의 수학은 강한 조건이 필요하지만… 생물학에서? Hebbian principle에 따르면 뉴런들은 비슷하게 뭉친다. 따라서 현실에서 Arora의 이론이 무리 없이 들어맞을 것이다?
- 이론은 spare하다. 그러나 현실의 컴퓨팅 자원은 dense하다. spare하면 cache hit overhead 짱짱. 결국 spare을 하기 불가능…
- The Inception architecture started out as a case study for assessing the hypothetical output of a sophisticated network topology construction algorithm that tries to approximate a sparse structure implied by [2] for vision networks and cov- ering the hypothesized outcome by dense, readily available components.
- Inception 아키텍처의 목표: spare이론을 dense현실에 근사해서 CV에 적용해보기.
Architectural Details
- The main idea of the Inception architecture is to consider how an optimal local sparse structure of a convolutional vi- sion network can be approximated and covered by readily available dense components
- Inception 아키텍처의 목표: spare이론을 dense현실에 근사해서 CV에 적용
- Arora et al. [2] suggests a layer-by layer construction where one should an- alyze the correlation statistics of the last layer and cluster them into groups of units with high correlation. These clus- ters form the units of the next layer and are connected to the units in the previous layer.
- 비슷한 정보를 가진 뉴런들이 모여 있다는 아이디어를 활용하자. 이전 레이어에서 비슷한 정보를 가진(correlated) 정보들이 모여있다. 그러면 그 parameter size을 다 쓰지 않고 합성하면 공간을 줄일 수 있다.
- 비슷한 정보라고 인식할 크기가 크면 정보들이 많이 손실 됨. (5 by 5) filter을 쓰면 25개의 칸이 1개의 정보로 축약 됨. 그래서 (1,1), (3,3), (5,5)필터들을 상황에 맞게? 사용함? 모여진 정보를 inception module이라고 부른다?
- It also means that the suggested architecture is a combination of all those layers with their output filter banks concatenated into a single output vector forming the input of the next stage.
- 11 33 55을 각각 convoluion해서 합치는 것이 output이 된다.
- 합치는 concatinate할 때 dimension이 같도록 path의 convolution 필터 크기 조절해야 한다. dimensio이 같아서 그냥 합치면 됨.
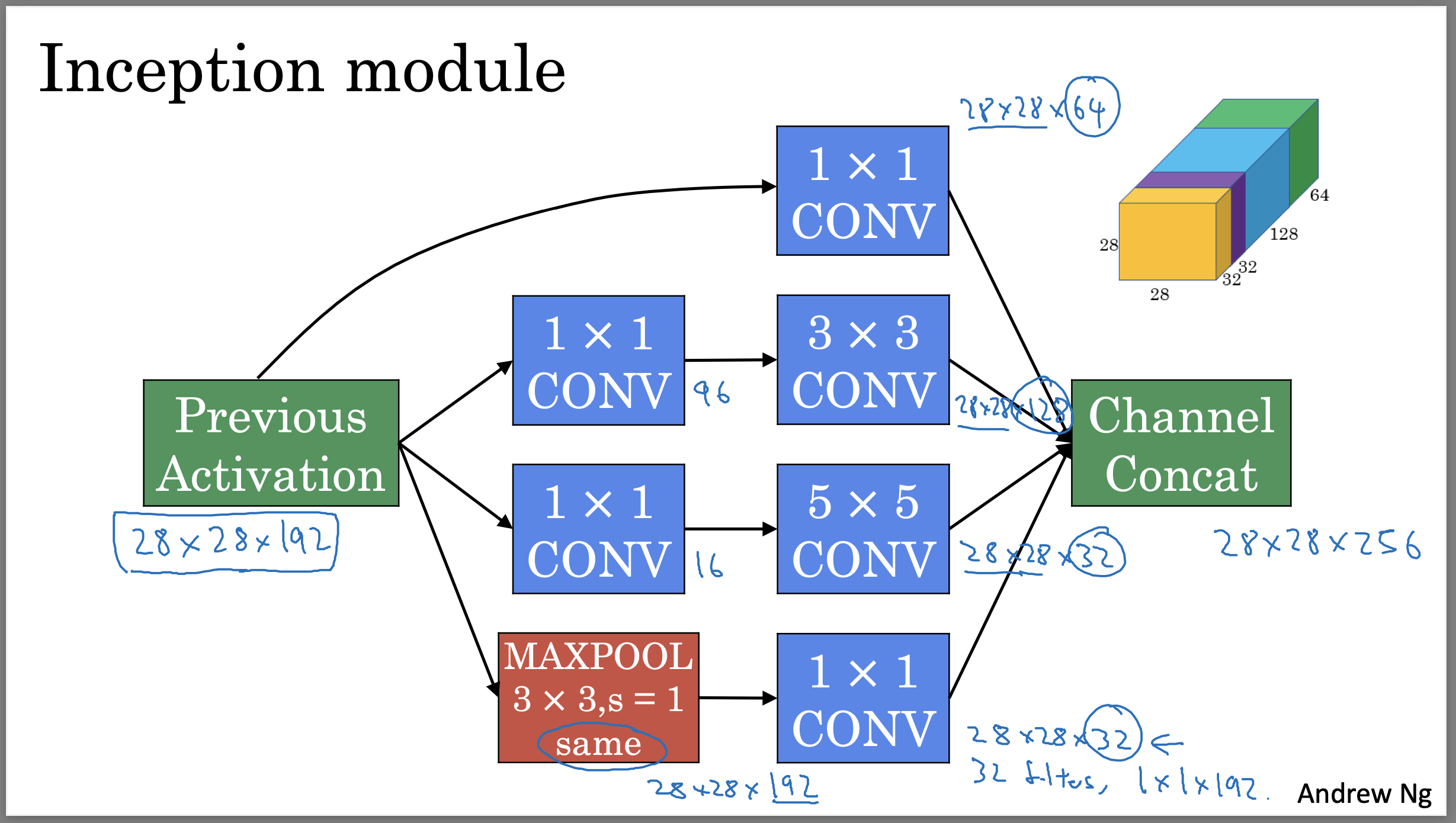 |
|---|
| Coursera의 Andrew Ng DLS 강의에서 가지고 옴. 이 그림은 논문의 fig 2 rediction dimension version이다. |
- Additionally, since pooling opera- tions have been essential for the success of current convo- lutional networks, it suggests that adding an alternative par- allel pooling path in each such stage should have additional beneficial effect, too (see Figure 2(a)).
- 요즘(이 논문을 쓰던 시기)의 CNN은 pooling이 필수. 그래서 우리도 사용했다!
- as features of higher abstraction are captured by higher lay- ers, their spatial concentration is expected to decrease. This suggests that the ratio of 3×3 and 5×5 convolutions should increase as we move to higher layers.
- 정보가 추상화될 수록 더 조밀하게 모아야 의미있다. 따라서 깊이가 깊어질 수록 더 많이 모으기 위해서 33 55 필터를 더 많이 사용할 것이다.
- 발생하는 문제점: 55 필터를 써도 이전 레이어의 채널의 수가 많으면 그래도 파라미터 수가 많아진다…
- 해결: 먼저 11 필터를 사용해서 채널 수를 낮춘다. 11필터를 쓰면 크기는 유지되지만, conv 레이어에서 output필터 수를 줄여서 전체 채널을 낮춘다. 추상적 정보를 집약시키는 것, 그리고 33,55을 적용. 이것이 fig 2(b)Inception module with dimensionality reduction.
- depth가 깊어서 vanishing gradient descent가 발생할 까봐 중간 중간에 classifier을 달아줌. auxiliary classifiers라고 부름. 중간 중간에서 gradient을 계산해서 back propagation 시킴. https://paperswithcode.com/method/auxiliary-classifier
사이즈를 spatial dimension이라고 부른다!
v3 assymetric conv.. fig 1보면 params 수 값 틀림. 파라미터 수 공식: h,w,c_prev * ffc_prevn_c이면, ffc_prevn_c가 파라미터 크기. 찾아야 할 것: 필터 크기 f, 인풋 필터 크기 c_prev, 필터 수 n_c. 왜? 정보 축약이 영역에 따라 다름. 하면 안되는 정보 축약도 존재. 부분만 conv 걸고 다시 다른 부분 conv. 게다가. 7 by 7 보다 7 by 1 * 1 by 7하면 파라미터 수도 더 줄어든다. https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/Szegedy_Rethinking_the_Inception_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf

Comments